
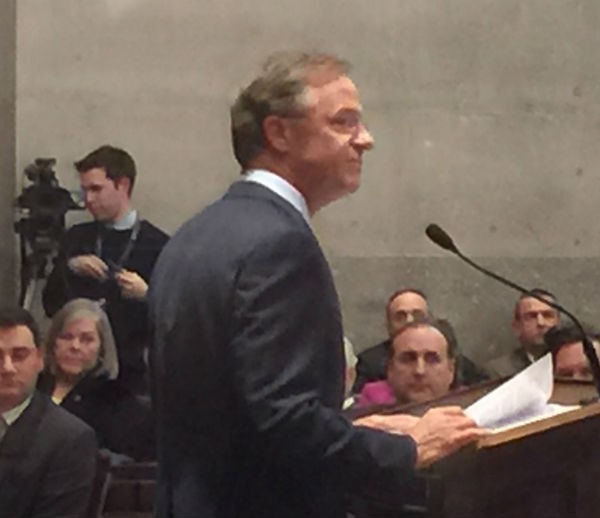
NASHVILLE — Like his 11-minute re-inauguration speech delivered two weeks ago, Governor Bill Haslam’s 15-minute opening address Monday night to this week’s special session on Insure Tennessee, his Medicaid expansion plan, was brief and to the point and couched in accommodationist rhetoric.
The previous speech had no particular mission in mind other than to hint at a more assertive second term: “[W]e haven’t had nearly high enough expectations of ourselves. In many ways, we’ve settled and haven’t lived up to our full potential. So one thing I can guarantee you that we are not going to do in the next four years is coast to the finish line.” But Monday night’s address was designed to spell out a key resolve that could be crucial to the success or failure of that race to the finish line.
The good news, from the governor’s point of view, was the prolonged standing ovation he received upon entering the chamber Monday night — a sign of the general good will that the General Assembly, on both sides of the political aisle, continues to extend to Haslam.
The bad news, from Haslam’s point of view, was that, by general agreement, he still has — in the words of state Representative Glen Casada (R-Franklin), who has been a prominent opponent of the governor’s plan — “his work cut out for him.” Said Casada about House prospects: “He needs 50 out of 99, and right now he doesn’t have it.”
That outlook was echoed by state Representative Craig Fitzhugh (D-Ripley), the Democrats’ House leader and a firm supporter of Insure Tennessee. Fitzhugh said, “He answered the questions. The main questions my friends on the Republican side have had. … The Republican caucus needs to show they have a concern for ‘the least of these’.'” The plan had “no downside,” said Fitzhugh, but, “I think he’s got a lot of work to do.”
State Senator Brian Kelsey (R-Germantown), chairman of the Senate Judiciary Committee and a foe, not just of the governor’s plan but of Medicaid expansion in general, said he thought opposition to Insure Tennessee was “mounting, the more we hear about it.”
Referencing a point Haslam had extemporized into his prepared remarks, to the effect that Republican governors had persistently expressed a wish to President Obama that Medicaid funding be presented to the states in the form of block grants, and that Insure Tennessee came close to that goal, Kelsey said, “My takeaway is this: The governor and I agree that we’d love to have a block grant in Tennessee, but that’s not what the president is offering.”
There were, however, signs that a bipartisan support coalition of Insure Tennessee from Republicans and Democrats (a distinct minority in the legislature that Haslam, however, had made a point of courting) might be possible.
In the immediate aftermath of the governor’s speech, state Rep. Antonio Parkinson, a Memphis Democrat, and state Rep. Mark White, a Republican who represents East Memphis and the suburbs, agreed that Haslam had made enough distinctions between Insure Tennessee and the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare) to coax reluctant GOP members to support the plan.
White himself had been one of those GOP members who’d been biding his time but now expressed support.”I think that was important for him to distance himself from the president,” White said. “He also gave a personal side. It’s not all politics. … The more you weigh it on our measuring scale, it weighs out that we need to do something.”
Two Democrats differed on the role of their party in the debate over Insure Tennessee. State Senator Lee Harris, the former city council member who was elected by Senate Democrats (5 members out of 33) to be minority leader, said, “It’s not about the Democrats. It’s not newsworthy what the Democrats are doing. That’s irrelevant. It’s about the Republicans. They have control of both chambers. If you’ve got control, you’ve got responsibility.”
State Representative G.A. Hardaway, another Memphis Democrat, begged to differ. Of the 26 Democrats in the 99-member House of Representatives, Hardaway said, “We hold the key in the House.”
• In his Monday night address opening the week of special session, the governor — Haslam being Haslam, a man of soft persuasion rather than faustian and bombast — artfully pitched an appeal that was simultaneously above partisan politics and designed to address what have been the main sticking points among GOP legislators.
The governor dutifully paid lip service to Republican talking points, loosing his own shots at what he consistently called Obamacare but taking pains to distinguish his own plan from the superstructure of the Affordable Care Act.
Haslam gave an explanation for why, in 2013, he had rejected the opportunity to expand Medicaid (TennCare in Tennessee) — an expansion that would have allowed the state to avail itself of about $1.5 billion annually, money which the state’s hospitals, charged with caring for indigent patients, contended they desperately needed.
He hadn’t accepted expansion then, the governor said, because “expanding a broken program doesn’t make sense. … But I also didn’t think that flat-out saying no to accepting federal dollars that Tennesseans are paying for — that are going to other states, and that could cover more Tennesseans who truly need our help — I didn’t think that made much sense either.”
Accordingly, he said, he decided to provide his own example of how a governmental health-care plan should work, spending the time since that decision in 2013 to devise what he told the assembled legislators is a two-year pilot program that has incorporated free-market principles, both through an optional voucher component for use with private insurance plans and through requiring co-pays and modest premiums — “skin in the game” — of those new insurees who chose to go through TennCare.
Haslam pointed out that Insure Tennessee would add no new costs to the state budget, since the Tennessee Hospital Association (THA) had guaranteed to pay any additional costs incurred once the federal government, after two years, dropped its own subsidy from 100 to 90 percent.
If either the federal government or the THA proved unable to follow through as promised, or if the state in two years’ time decided Insure Tennessee wasn’t a good fit, the state had been assured by court decisions and the state attorney general’s advice that it could discontinue the plan.
(Pointedly, the governor, in giving the address, dropped this line from his prepared remarks: “I understand the concern, but I think it’s worthy of mention that the United States of America has never missed a scheduled Medicaid payment.”)
As for the professed concern of Insure Tennessee skeptics regarding the pain of having to discontinue coverage for new insurees after two years, Haslam said, “If you gave your loved one an option: You can have health coverage now to address your very real need and with that the possibility that you might lose it in the future, or you could never have it, which would you choose? If you think about your loved one, I bet the answer is simple.”
Ultimately, said Haslam, the state simply had an obligation to the unfortunate and the indigent, one based in commonly held spiritual precepts. “My faith doesn’t allow me to walk on the other side of the road and ignore a need that can be met — particularly in this case, when the need is Tennesseans who have life-threatening situations without access to health care.”
• Back in Memphis, pent-up controversy was also moving toward some overdue discussion. On Wednesday’s committee agenda of the Shelby County Commission is a call for open discussion of the future of the Economic Development Growth Engine (EDGE), which guides industrial and business expansion and awards economic incentives toward that end.
Republican member Steve Basar, chair of the commission’s economic development committee and the commission’s ex officio member of the 11-member EDGE board, placed the discussion item. Basar said he heard “rumblings” of discontent about EDGE on the commission, including possible calls for the board’s abolition, and, as an EDGE supporter, wanted to address it.
Much of the discontent was an adverse reaction to the EDGE board’s recent decisions on PILOTs (payment-in-lieu-of-taxes), but Basar said only minor modifications were needed.


 Skip Hooper, Courtesy of Theatre Memphis
Skip Hooper, Courtesy of Theatre Memphis 
 Larry Kuzniewski
Larry Kuzniewski  Greg Cravens
Greg Cravens 
 JB
JB 
