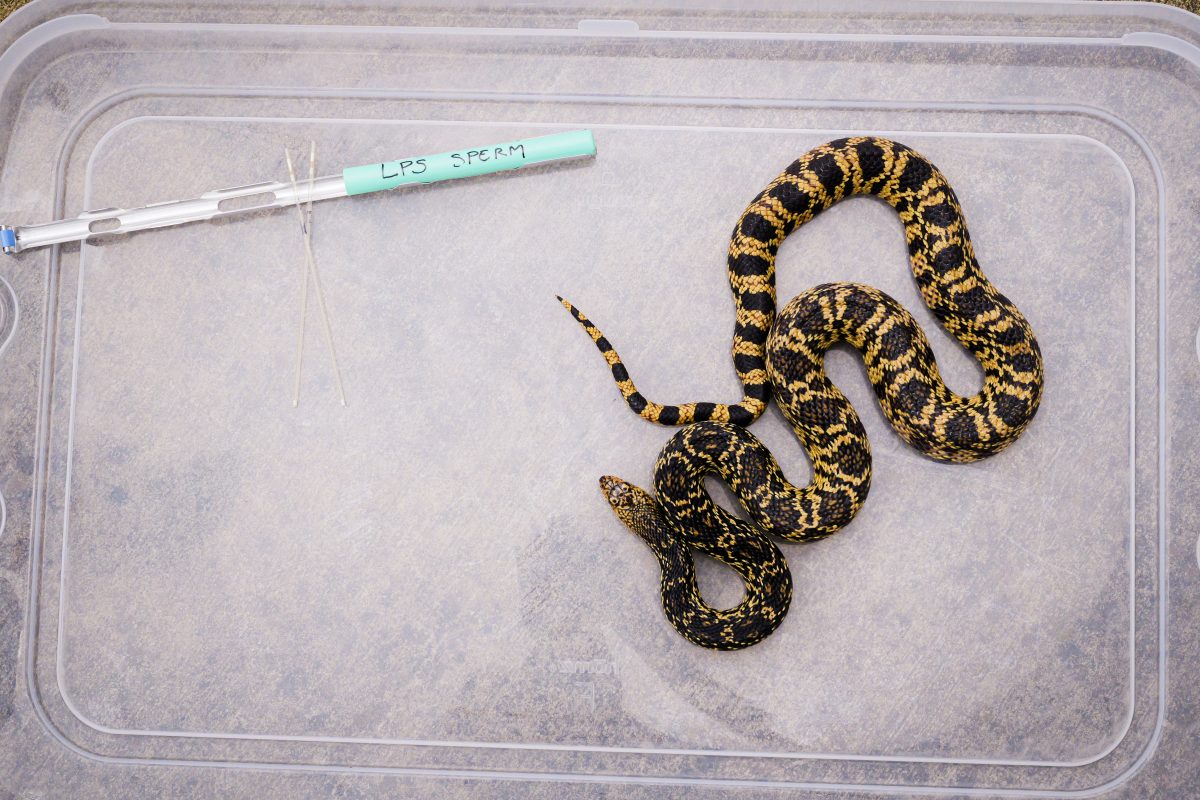
Scientists at the Memphis Zoo have — for the first time in the world — successfully produced the first reptile offspring using frozen semen and artificial insemination.
The team achieved the feat through its work to preserve the Louisiana pinesnake. The Memphis Zoo’s Science team is led by Dr. Steve Reichling, Beth Roberts, and previous post-doctoral scientist Dr. Mark Sandfoss. The team collected, froze, and later thawed semen, which was then used to successfully inseminate a female Louisiana pinesnake.
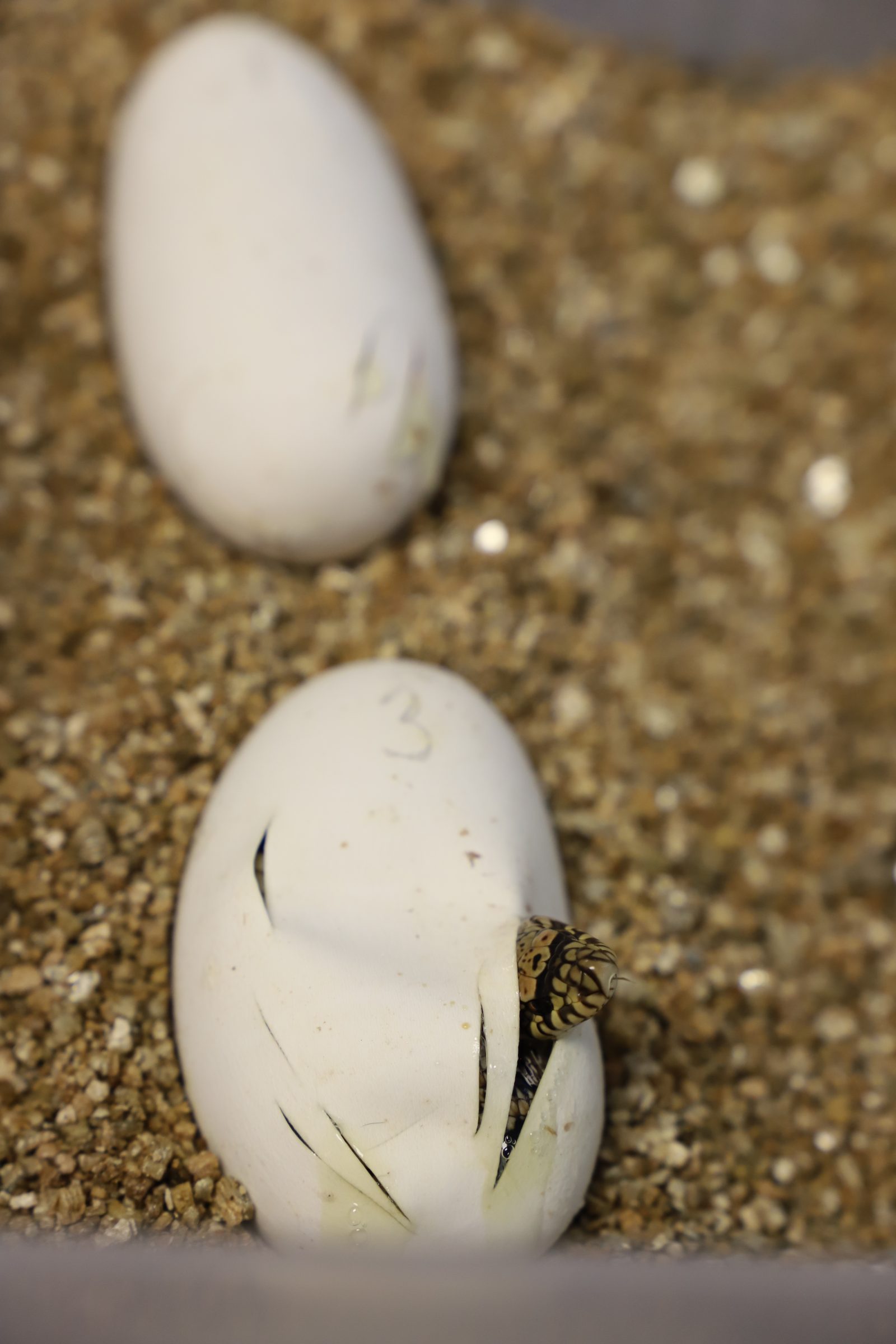

“Today, the future of endangered reptiles got a little brighter,” Reichling said.
Reptiles are often overlooked in such breeding methods, the zoo said in a news release. The concept of a “frozen zoo” has primarily focused on mammals, birds, and amphibians. The zoo’s method used in snakes demonstrated its potential in reptile conservation worldwide, it said.
“The emergence of these three hatchlings summed up five years of reproductive research and 30 years of Memphis Zoo’s use of cutting-edge science and dedication to save the Louisiana pinesnake from extinction,” said Roberts, Senior Reproductive Scientist at Memphis Zoo.
Testing at Auburn University confirmed that the offspring were sired by the male snake donor.
“We see this success as a huge step forward to enable future efforts to improve the genetic health of this species and other threatened reptile species,” said Dr. Tonia Schwartz, Associate Professor in Auburn’s Department of Biological Sciences.
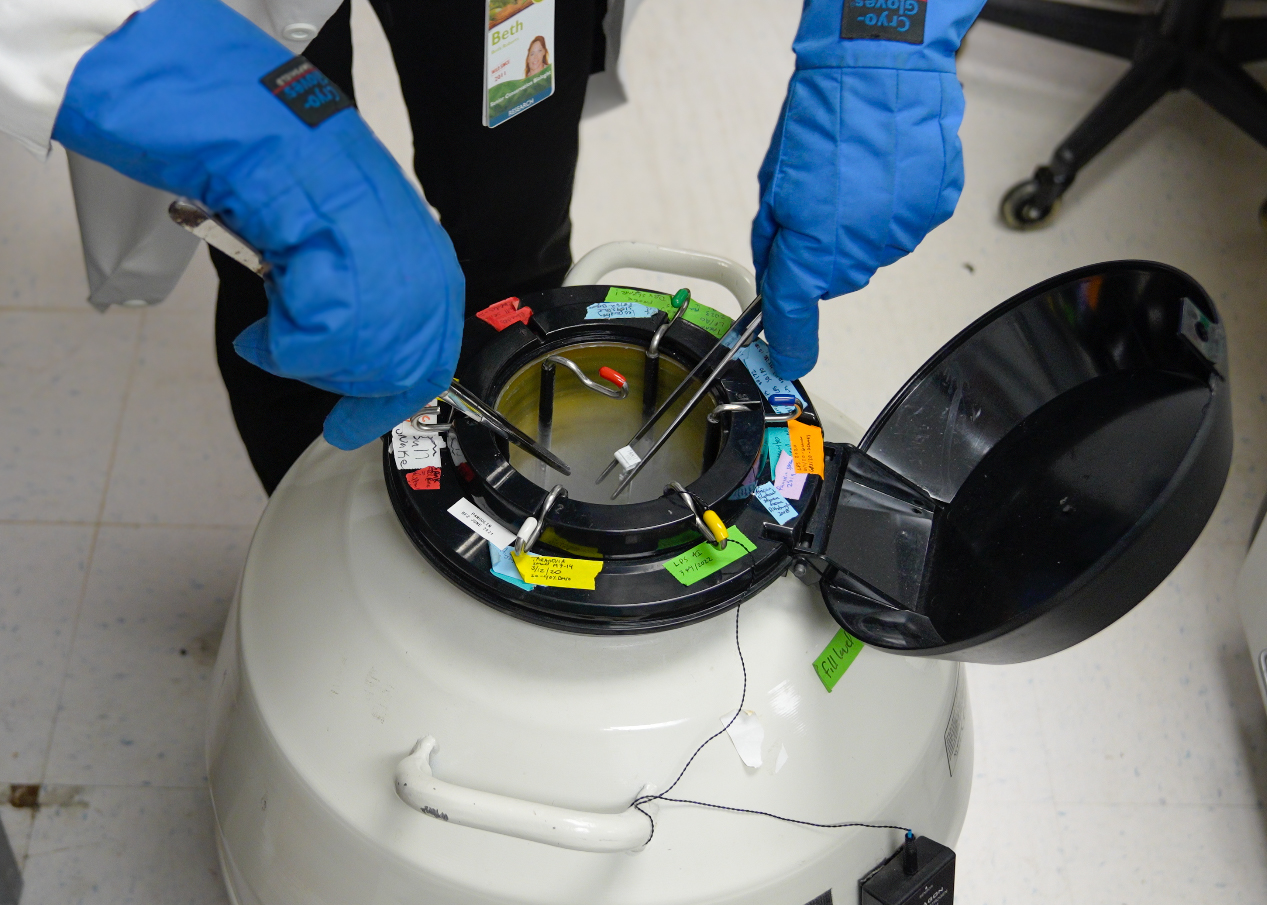

The Louisiana pinesnake is one of the rarest snakes in North America. Habitat loss continues to threaten their survival. So, researchers said the ability to use frozen semen offers new hope for maintaining genetic diversity in the species and ensuring its long-term survival. The zoo team plans to continue its work in reptile conservation, building on its research, and collaborating with other institutions worldwide.
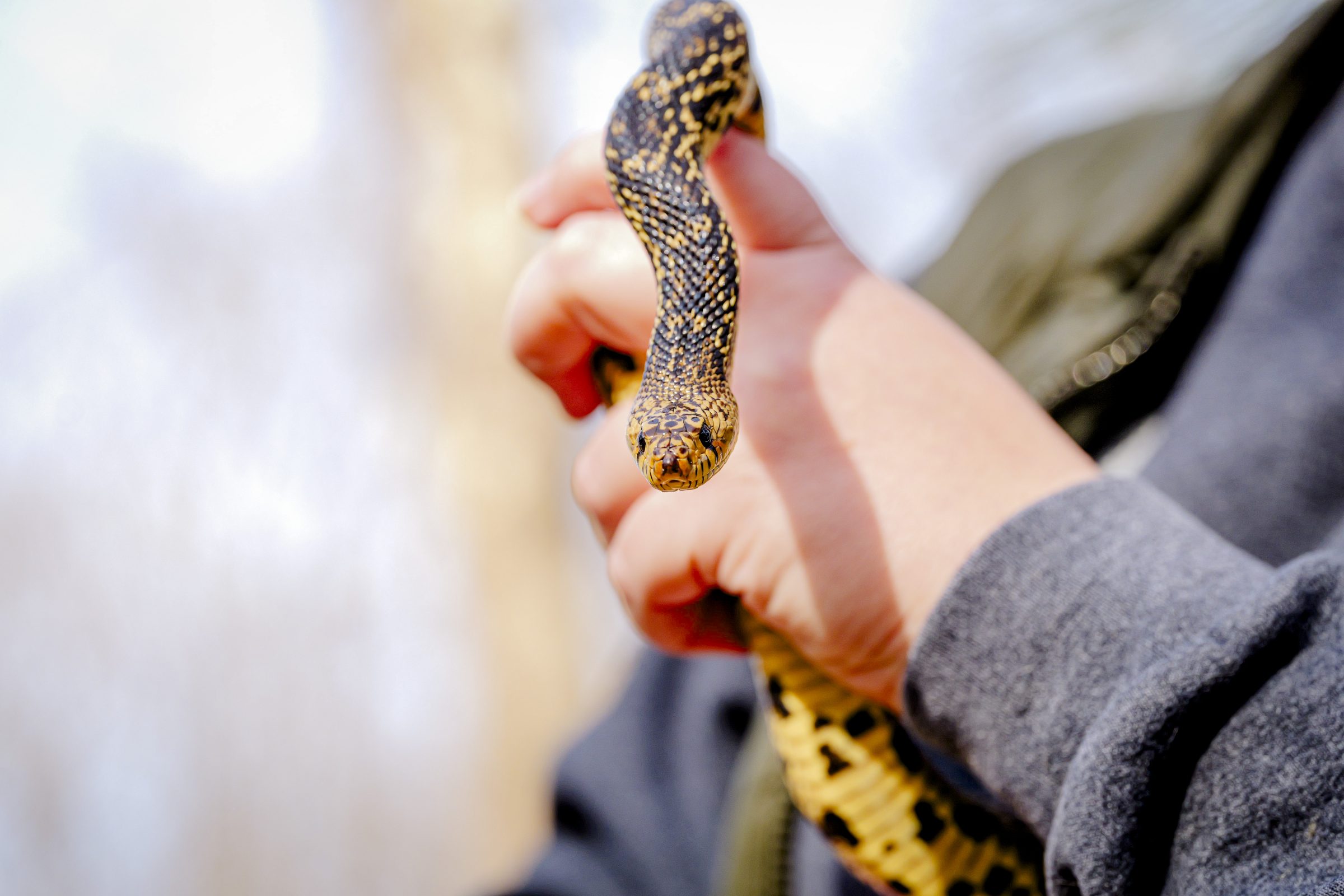

“Memphis Zoo is setting an example for the global community,” said Sandfoss, who spearheaded the research. “We’ve shown that it’s possible to use cryopreserved genetic material to aid in the recovery of an endangered species, paving the way for similar efforts with other reptile species in the future.”